Agentic AI vs. AI Agent: Understanding the Key Differences
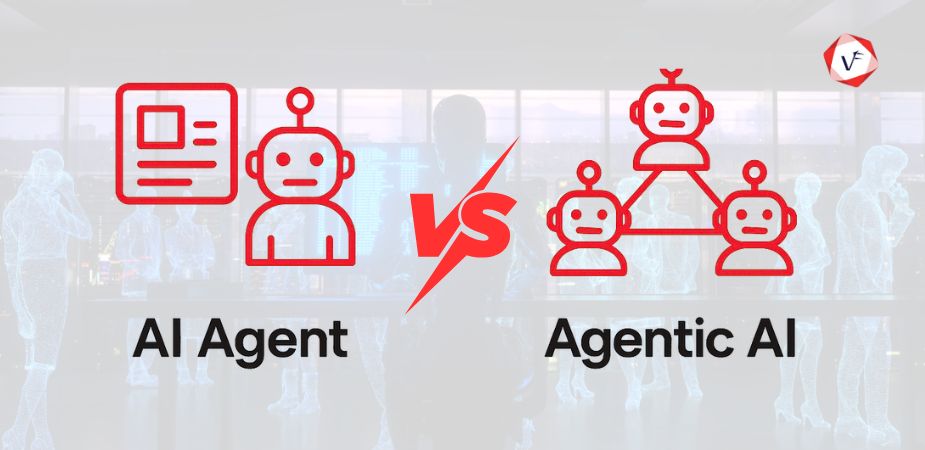
Quick Answer: Agentic AI refers to autonomous systems with proactive decision-making capabilities and distributed architectures that adapt to complex environments. AI Agents are specialized, modular systems that operate within defined parameters using structured protocols. The key difference lies in autonomy, adaptability, and operational scope—Agentic AI is proactive and exploratory, while AI Agents are reliable and task-specific.
The artificial intelligence industry continues to expand rapidly, introducing new concepts and terminologies that often create confusion among professionals and enthusiasts alike. Two frequently misunderstood concepts are “Agentic AI” and “AI Agent,” which, despite their similar names, represent fundamentally different approaches to artificial intelligence implementation.
Understanding the distinction between agentic AI and AI agent becomes crucial for organizations seeking to implement the most appropriate AI solutions for their specific needs. While both concepts involve autonomous decision-making capabilities, their architectural foundations, operational methodologies, and practical applications differ significantly. This comprehensive exploration will clarify these differences and help readers make informed decisions about which approach best serves their objectives.
What Makes AI “Agentic”
Defining Agentic AI Systems
Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that demonstrate autonomous agency in their decision-making processes. These systems possess the ability to independently analyze situations, formulate strategies, and execute actions without constant human intervention. Agentic AI systems exhibit characteristics similar to human agency, including goal-directed behavior, adaptability, and the capacity to learn from their environment.
Proactive Nature and Autonomous Behavior
The core principle behind agentic AI lies in its proactive nature. Rather than simply responding to predefined inputs, agentic AI systems actively seek information, identify opportunities, and initiate actions that align with their programmed objectives. This autonomous behavior distinguishes agentic AI from traditional reactive AI systems that merely process inputs and generate outputs based on predetermined rules.
Learning and Adaptation Capabilities
Agentic AI systems incorporate sophisticated machine learning algorithms that enable them to adapt their behavior based on changing circumstances. These systems can modify their strategies, adjust their priorities, and even redefine their approaches when encountering novel situations. The learning capability inherent in agentic AI allows these systems to become more effective over time, continuously improving their performance through experience.
Architectural Differences: Structure & Implementation
- Agentic AI Architecture: Distributed and Flexible
The architectural distinctions between agentic AI and AI agent systems reflect their different operational philosophies. Agentic AI systems typically employ distributed architectures that support complex, interconnected decision-making processes. These systems integrate multiple AI technologies, including natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics, to create comprehensive autonomous capabilities.
Agentic AI architectures prioritize flexibility and adaptability, incorporating feedback loops and learning mechanisms that enable continuous improvement. The system design accommodates emergent behaviors and unexpected outcomes, allowing agentic AI to discover novel solutions and approaches that weren’t explicitly programmed by their creators.
- AI Agent Architecture: Structured and Modular
AI agent architectures, conversely, follow more structured and hierarchical designs. Each AI agent operates within clearly defined boundaries and communicates with other system components through established interfaces and protocols. This architectural approach ensures predictable behavior and facilitates easier troubleshooting and maintenance.
The modular design of AI agent systems enables organizations to implement incremental upgrades and modifications without disrupting the entire system. This scalability makes AI agents particularly attractive for enterprise applications where stability and reliability are paramount concerns.
Operational Characteristics: How They Function
- Agentic AI Operational Behavior
Agentic AI systems demonstrate remarkable operational autonomy, capable of initiating actions, making complex decisions, and adapting their behavior based on environmental feedback. These systems actively monitor their surroundings, identify relevant information, and pursue their objectives through strategic planning and execution.
The operational behavior of agentic AI systems closely resembles human-like reasoning processes. They can weigh multiple factors simultaneously, consider long-term consequences, and make trade-offs between competing objectives. This sophisticated decision-making capability enables agentic AI to handle complex, unstructured problems that would challenge traditional AI approaches.
- AI Agent Operational Behavior
AI agents operate more systematically, following predetermined protocols and decision trees to process information and generate responses. While AI agents can exhibit intelligent behavior within their designated domains, their operational scope remains more limited compared to agentic AI systems.
The collaborative potential of AI agents represents one of their strongest operational characteristics. Multiple AI agents can work together, sharing information and coordinating their actions to achieve collective goals that exceed the capabilities of individual agents.
Real-World Applications: Where Each Approach Excels
- Agentic AI Use Cases
Agentic AI finds particular success in applications requiring high levels of autonomy and adaptability. Autonomous vehicles represent a prime example of agentic AI implementation, where systems must continuously analyze complex traffic situations, make split-second decisions, and adapt to unexpected circumstances while maintaining passenger safety.
Financial trading systems also benefit from agentic AI capabilities, as these systems must analyze market conditions, identify opportunities, and execute trades autonomously while managing risk and responding to rapidly changing market dynamics. The proactive nature of agentic AI enables these systems to capitalize on fleeting opportunities that human traders might miss.
- AI Agent Use Cases
AI agents excel in applications requiring specialized expertise and reliable performance within defined parameters. Customer service chatbots represent successful AI agent implementations, where each agent handles specific types of inquiries using predetermined knowledge bases and response protocols.
Manufacturing quality control systems effectively utilize AI agents to inspect products, identify defects, and trigger appropriate responses based on established criteria. The consistency and reliability of AI agents make them ideal for such applications where predictable outcomes are essential.
Decision-Making Frameworks: Autonomous vs. Structured Approaches
- Agentic AI Decision-Making Process
The decision-making processes employed by agentic AI and AI agent systems reflect their fundamental philosophical differences. Agentic AI systems utilize sophisticated reasoning frameworks that incorporate uncertainty, probability, and multi-criteria analysis to make decisions in complex, ambiguous situations.
These systems can handle incomplete information, make assumptions based on available data, and adjust their decisions as new information becomes available. The decision-making process in agentic AI systems often involves exploring multiple potential outcomes and selecting the most promising approaches based on their assessment of likely success.
- AI Agent Decision-Making Process
AI agents typically employ more structured decision-making frameworks based on rule-based systems, decision trees, or trained neural networks. These frameworks provide consistent, predictable outcomes but may lack the flexibility to handle truly novel situations that fall outside their training parameters.
The structured approach used by AI agents offers advantages in applications where consistency and auditability are important requirements. Organizations can more easily understand and verify the decision-making process of AI agents, making them suitable for regulated industries and applications where accountability is crucial.
Integration Challenges & Opportunities
- Agentic AI Integration Considerations
Implementing agentic AI systems presents unique integration challenges due to their autonomous nature and complex behavioral patterns. Organizations must carefully consider how agentic AI systems will interact with existing infrastructure, human personnel, and established business processes.
The unpredictable nature of agentic AI behavior, while valuable for discovering innovative solutions, can create difficulties in maintaining system stability and ensuring compliance with organizational policies. Companies implementing agentic AI must develop robust monitoring and governance frameworks to manage these autonomous systems effectively.
- AI Agent Integration Considerations
AI agent integration typically proves more straightforward due to their modular design and predictable behavior patterns. Organizations can implement AI agents incrementally, gradually expanding their capabilities and coverage areas while maintaining system stability and control.
The standardized interfaces and communication protocols used by AI agents facilitate integration with existing enterprise systems, making them attractive options for organizations seeking to enhance their current operations without major infrastructure overhauls.
Future Implications & Considerations
- The Evolution of AI Technologies
As artificial intelligence technology continues advancing, the distinction between agentic AI and AI agent approaches may become less pronounced. Hybrid systems that combine the autonomy of agentic AI with the reliability of AI agents are already emerging, offering organizations the benefits of both approaches.
- Governance and Capability Advancement
The development of more sophisticated AI governance frameworks will likely expand the practical applications of agentic AI systems, addressing current concerns about unpredictability and control. Similarly, advances in AI agent technology may increase their autonomy and flexibility, bringing them closer to agentic AI capabilities.
- Strategic Implementation Planning
Organizations planning their AI implementation strategies should carefully consider their specific requirements, risk tolerance, and long-term objectives when choosing between agentic AI and AI agent approaches. The decision should align with organizational capabilities, regulatory requirements, and strategic goals.
Performance Metrics & Evaluation Criteria
- Evaluating Agentic AI Performance
Measuring the effectiveness of agentic AI versus AI agent implementations requires different evaluation frameworks. Agentic AI systems demand metrics that capture their adaptive capabilities, learning progression, and autonomous decision quality over time. Traditional performance indicators may prove inadequate for assessing systems that continuously modify their behavior and strategies.
Agentic AI evaluation focuses on outcome optimization, behavioral consistency under varying conditions, and the system’s ability to discover novel solutions. Success metrics often include goal achievement rates, adaptation speed to environmental changes, and the quality of autonomous decisions made without human intervention. These systems require longitudinal assessment approaches that track performance improvements across extended operational periods.
- Evaluating AI Agent Performance
AI agent evaluation, conversely, emphasizes reliability, accuracy, and consistency within defined operational parameters. Standard metrics include task completion rates, error frequencies, response times, and adherence to predetermined protocols. AI agents benefit from more straightforward evaluation processes since their behavior patterns remain more predictable and measurable using conventional testing methodologies.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right AI Approach
The distinction between agentic AI and AI agent represents more than semantic differences; it reflects fundamentally different approaches to artificial intelligence implementation. Agentic AI offers autonomous, adaptive capabilities ideal for complex, unpredictable environments, while AI agents provide reliable, specialized functionality within structured frameworks.
Organizations must carefully evaluate their specific needs, constraints, and objectives when selecting the appropriate approach. Both technologies offer significant value in their respective domains, and the choice depends largely on application requirements and organizational readiness.
For companies seeking expert guidance in navigating these AI implementation decisions, Vofox’s AI/ML development services provide comprehensive solutions tailored to specific business needs and objectives. Contact us today to learn how you can begin your Vofox AI journey.